Published
- 2 min read
Network time delay using Dijkastra to find time to reach all vertices

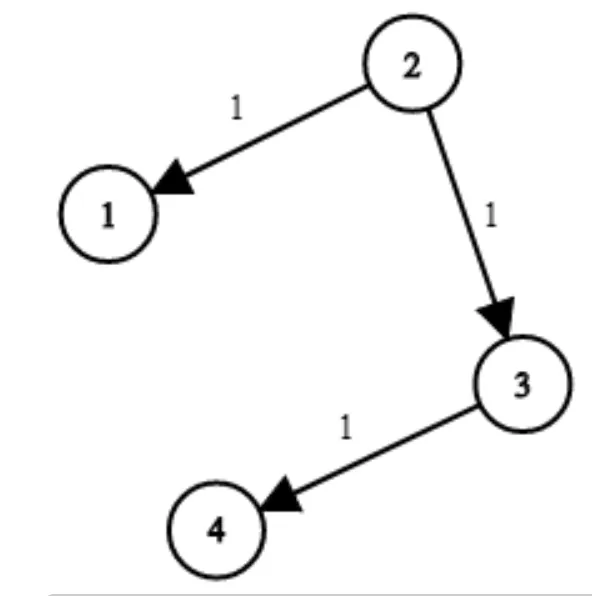
Network time delay problem
Given a graph with vertices and the time it takes to visit each of them from a given source, print the minimum time it takes to visit the destination This alogirthm can be solved in multiple ways the, one of the the way is to use BFS with calculation of minimum of cost at each level(neighbour) Dijkastra alogrithm uses greedy approach, each step selects minimum weight from the current vertice to find minimum cost/path to next vertice.
Note: Dijkastra only solves path with positive weight and keep the cost minimum, it isnt trying to solve shortest path
We create adjacency list of time it takes to visit each vertices and then place checks in the code to find at each level whats the minimum time at each vertice
private int minTimeToReachNodes(int totalNodes, int source, int [][] graphWithWeights){
//Nodes on the same level will receive the signal together, as the level changes add the weight of that to the list
int maxValue = 0;
Map<Integer, List<Pair>> adjacencyList = new HashMap();
for (int i=0; i<graphWithWeights.length; i++) {
List<Pair> l = new ArrayList<>();
adjacencyList.put(graphWithWeights[i][0], l);
}
for (int i=0; i < graphWithWeights.length ; i++) {
List<Pair> list = adjacencyList.get(graphWithWeights[i][0]);
list.add(new Pair(graphWithWeights[i][1], graphWithWeights[i][2]));
adjacencyList.put(graphWithWeights[i][0], list);
}
//when to use array[], when to not use it.
int timeAtEachNode [] = new int[totalNodes + 1];
for(int i=1; i < timeAtEachNode.length; i++){
timeAtEachNode[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //Thinking that it takes infinite time to reach a node from another
}
Queue<int []> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new int[]{source, 0});
timeAtEachNode[source] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] currentSource = q.poll();
int currentTime = currentSource[1];
if(!adjacencyList.containsKey(currentSource[0])) {
continue; //since graph is directed it will having nodes which arent part of adjacency list
}
System.out.println("Current node : "+ currentSource[0] + " currentTime " + currentTime);
List<Pair> neighbours = adjacencyList.get(currentSource[0]);
for (Pair neighbour : neighbours) {
int nextReachableNode = neighbour.node;
int timeItTakes = neighbour.val + currentTime;
if(timeAtEachNode[nextReachableNode] > timeItTakes) { //Like this we would be choosing only 1 neighbour
timeAtEachNode[nextReachableNode] = timeItTakes;
q.add(new int[]{nextReachableNode, timeAtEachNode[nextReachableNode]});
}
}
}
for (int i=0; i<timeAtEachNode.length;i++) {
System.out.println("timeAtEachNode : " + timeAtEachNode[i]);
if(timeAtEachNode[i] == Integer.MAX_VALUE){
return -1;
} else {
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, timeAtEachNode[i]);
}
}
return maxValue;
}
class MyPair {
int node;
int weight;
MyPair(int n, int w){
this.node = n;
this.weight = w;
}
}